Inspect the driveway for potholes, Water woes, ground consistency, drainage, run downs and weeds.
Ground Consistency
A) Gravel
Granular base and sub base applications generally consist of sand mixed with gravel.
Granular fill must consist of pit-run gravel, sand or crushed gravel placed upon the prepared areas.
B) Gravel Sizes. Driveway gravel should be relatively large, between about 10 mm and 20 mm in diameter, as compared to the gravel used for footpaths, which is typically 6 mm to 10 mm in diameter. Another factor to consider is the amount of very small granular material, called “fines,” in the gravel.
C) Layer depth of the gravel should be at least 100 mm to 150 mm. To do two to three layers, each layer will need to be 100 to 150 mm thick, so calculate each layer separately.
Important Notes:
River rock is not appropriate for a driveway. … Top layer choices for gravel driveways might include crushed shale, limestone, granite and concrete, along with other types of gravel in various colors to meet your aesthetic needs.
Using 50 mm for the depth, the following measurements are a guide to the amount of gravel coverage per ton: 1/4 to 1/2 inch gravel, 100 square feet per ton(9.3m2); 1/2 to 1 inch gravel, 90 square feet per ton(8.4m2); and 1 1/2 to 2 inches gravel, 80 square feet per ton
Gravel should be raked up onto the driveway, and tamped down until it’s flat. Then the gravel should be wetted down with a hose, allowing the rock to shift and the dirt to accept the gravel once again. Don’t use too much water, because you might cause the driveway to shift and the dirt to run.
C) Clay
Fill dirt containing more than 50 percent clayis useful as a base for pathways and garden structures, such as sheds, but not for filling planting areas. It is a very poor subsoil and not ideal for support, as foundations are most stable on soil that does not shift or change structure. … These extreme changes put a great deal of pressure on foundations, causing them to move up and down, and eventually crack, making clay a poor soil for support.
With proper preparation, however, it’s possible to pour a slab on clay soil without encountering these problems. … This method will prevent the clay soil from absorbing moisture from your concrete. Place 3/8-inch or 1/2-inch rebar inside the frame to provide additional strength to your concrete slab
Foundations on clay soil. … Clay soils are made up of 40% water, but trees can change this amount differently throughout the year – causing the soil to shrink or swell with enough force to affect the foundations of a building and so it’s vital that the foundation is the right depth to prevent movement.
D) Stone is best for drainage
The stone should be no less than 3/4” and dense (we suggest Granite, or River Gravel) so it will allow good water flow. Lime Rock, although inexpensive, is a poor choice for a French Drain because it will begin to deteriorate over time and eventually begin to pack down and restrict flow.
Gravel used for this layer is typically 1/2 inch to 1 inch across — the larger it is, the better the water flow and less chance of clogs and blockages. For a French drain without a perforated pipe, opt for even larger gravel, such as 1 1/2 inches across
Weeds. Treat weeds with the appropriate weed killer.
Long-term solutions to gravel driveway maintenance
Machinery that can spread and compact gravel to form a smooth surface and reduce loose layers of rock.
The proper care and feeding of a pothole
widen the pothole by taking out the entire section, then fill in the hole with layers of gravel, compacting each as you go.
Water woes
Problems with ruts, washouts, and birm, which probably have drainage issues. either to add enough gravel to make your drive higher than the areas surrounding it, or install a culvert or ditch to pull the water around the place where it flows over the gravel
Geotextile fabric, anyone?
When all else fails. layer to the substrata. It corrects unstable, soggy soil.
Consider excavation
Extremely rutted gravel drive with weeds and a sub-grade that’s unstable should be redone completely
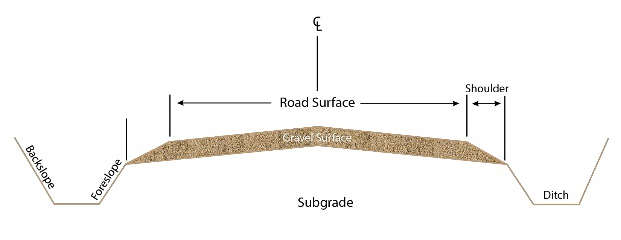
A crowned surface is necessary for drainage but if it’s too high, it can lead to unsafe driving conditions. An excessive slope will cause drivers to drift towards the shoulder. 1.27 cm of crown per 30 cm on the cross slope is recommended.
horizontal angle for the moldboard is between 30 and 45 degrees
Example
2.5m wide driveway
crown to end 1.25m
1200 / 300 = 4
4×12.7mm = 51mm down on side from to of crown
Ditches
The ditches on either side of the road need to be clear of debris to ensure proper drainage. The minimum recommended depth and width for these ditches is 30 cm. Areas with heavy water runoff will require larger ditches.
Potholes
Grade the potholes (if possible) The road needs to be graded to the same depth as the pothole. Never fill a pothole in with loose aggregate, this won’t last under traffic wear and the pothole will quickly reform.
Fill the pothole with coarse gravel up to about three inches below the surface of the driveway. Next you should compact the coarse gravel. For a dirt driveway, fill the hole with dirt up to three to four inches above the desired surface level.

